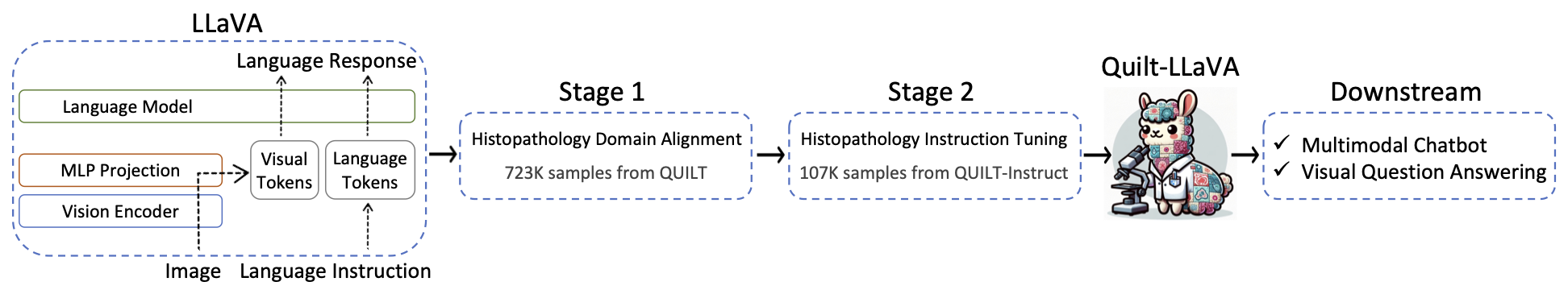
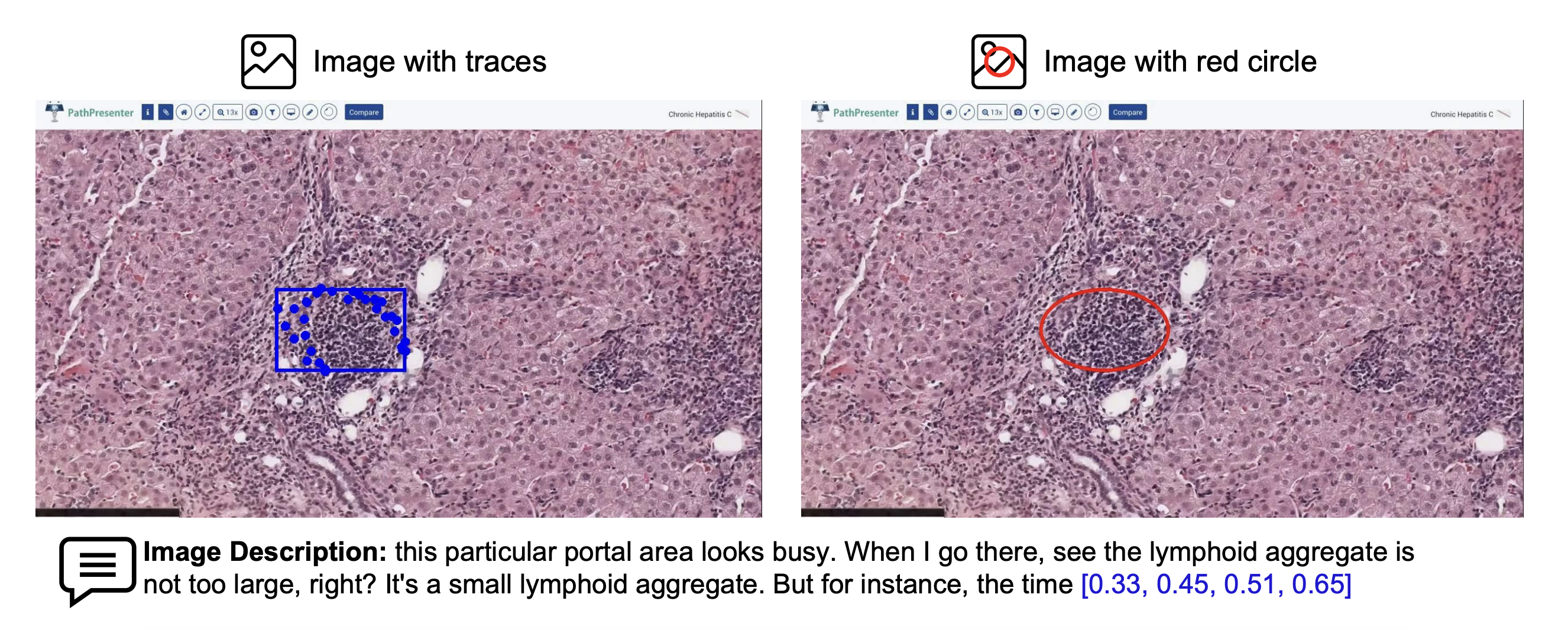
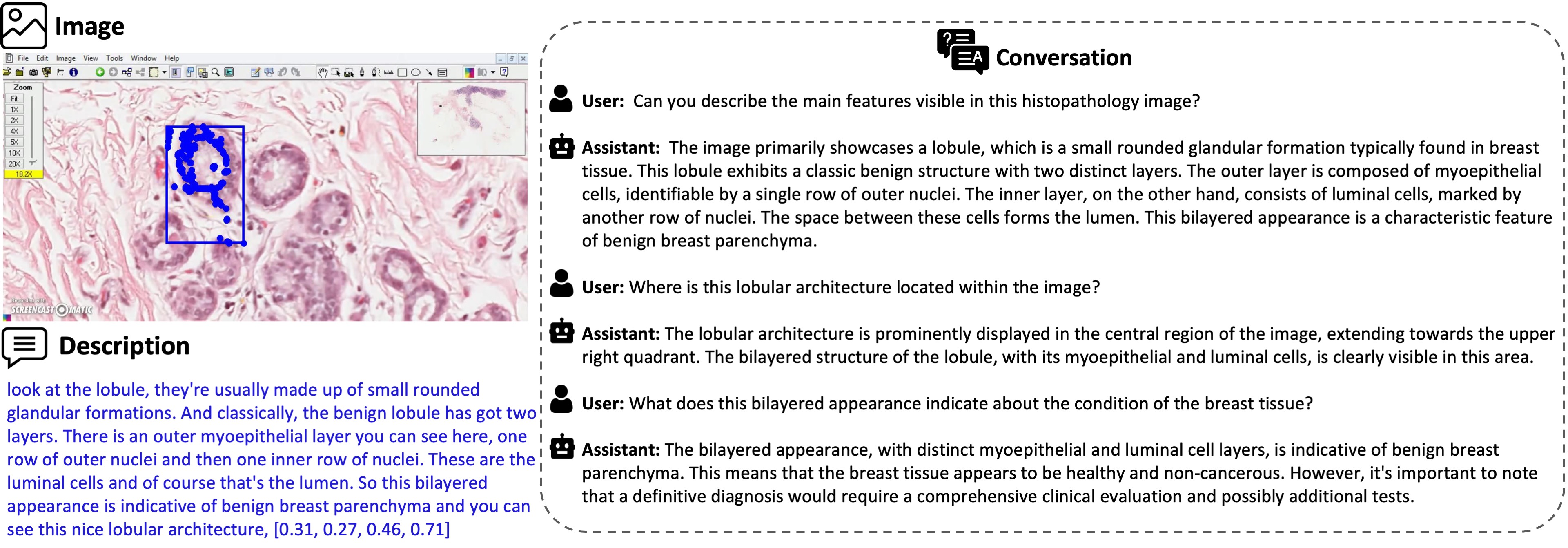
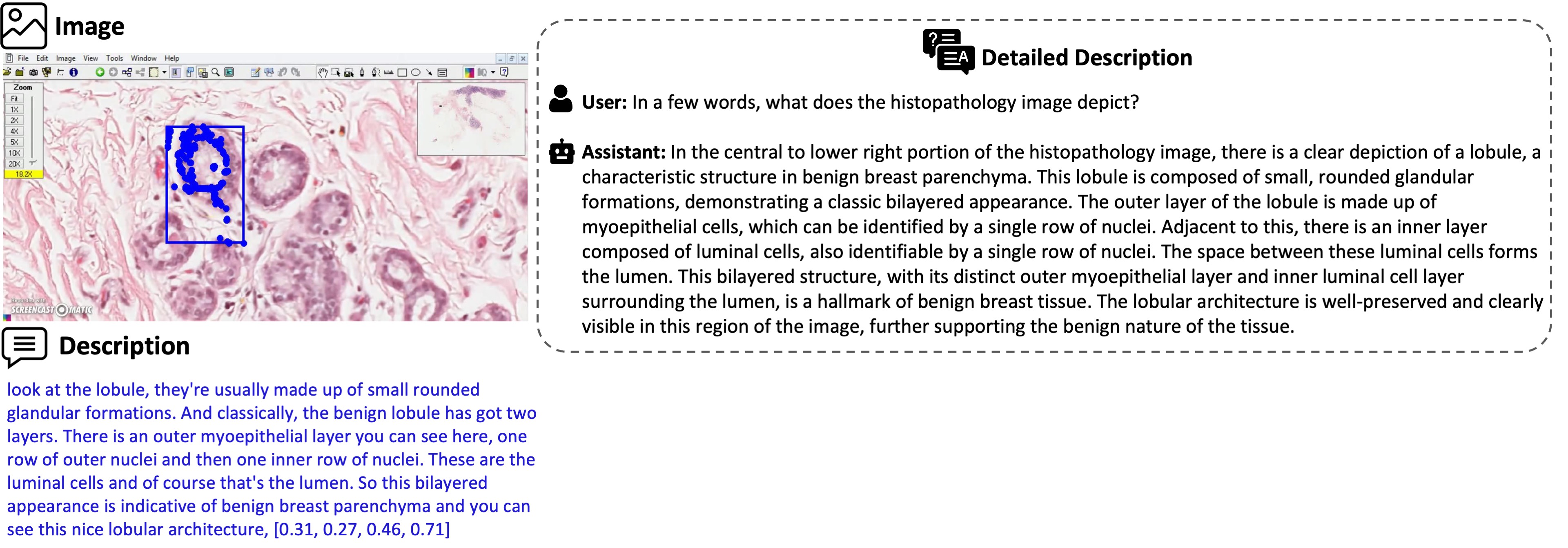
Similar to LLaVA-Med, we use conversation and detailed description based prompts (We call these independent prompts, where each image/caption pair is considered independent to one another), where we utilize GPT-4 to generate Q&A pairs from image captions. However unlike LLaVA-Med, which lacks spatial groundings, we extract mouse pointers to ground narrator's speech into spatial regions of images, leading to better spatial awareness.
Traditional image-caption datasets often consist of pairs that lack contextual connection, limiting the Q/A pairs generated by GPT-4 to the context of a single image. This is particularly a limitation for histopathology images, which require holistic analysis beyond a single image patch. To overcome this, we propose reasoning-based prompting techniques: Complex Reasoning and Iterative Abductive Reasoning, where we distill the global facts and the diagnosis from the broader video content, and leverage these when prompting GPT-4, enabling it to extrapolate in a contextually anchored manner, thereby reducing the risk of hallucinations.
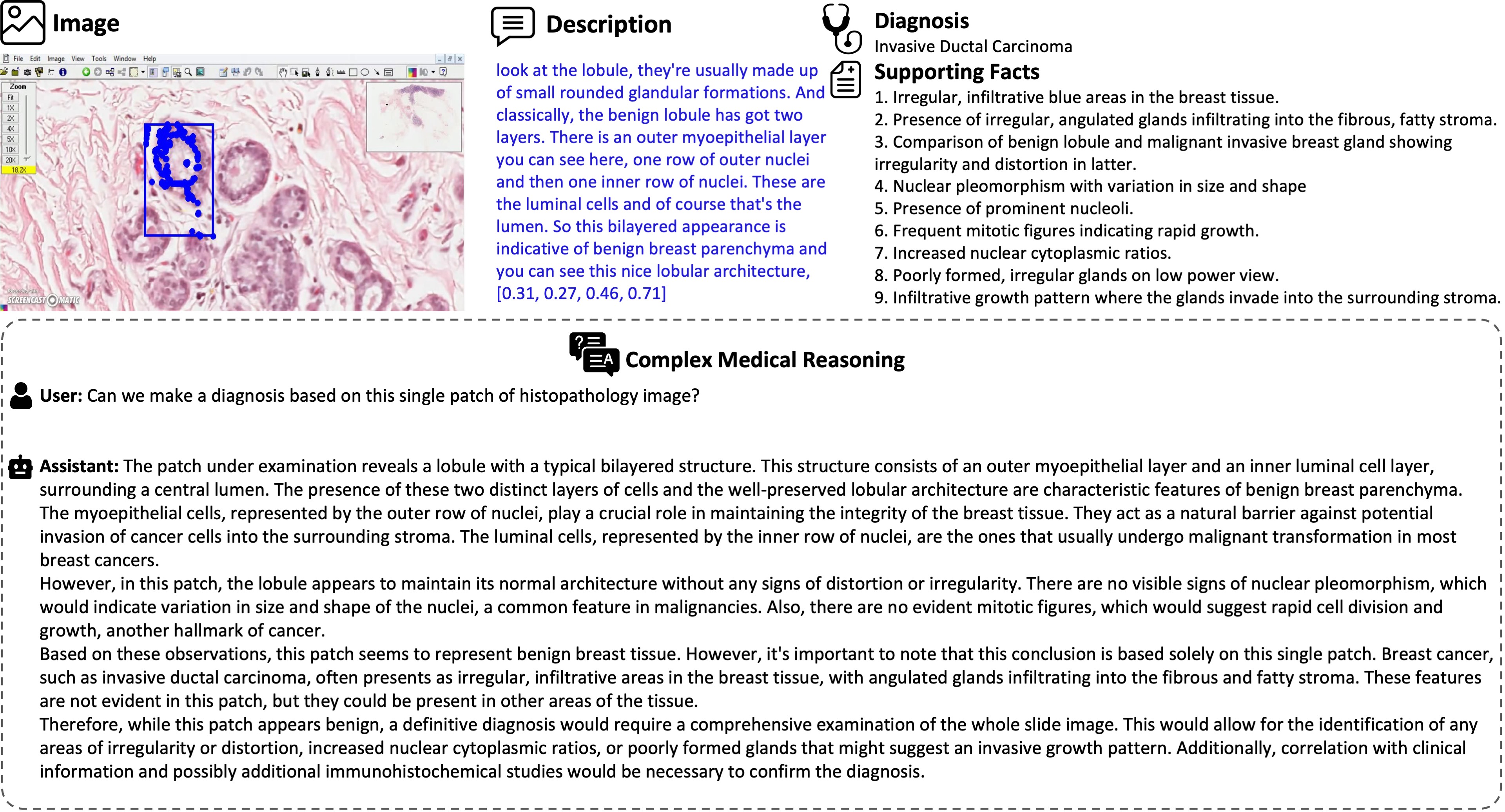
In complex reasoning, given a caption, along with a diagnosis and contributory facts, we prompt GPT-4 in a diagnostic reasoning task designed to extrapolate beyond the immediate context of the given caption. More broadly, we instruct GPT-4 to utilize its inherent medical knowledge to interpret the contents of a single image caption, while subconsciously incorporating the diagnosis and supporting facts extracted from the broader video.
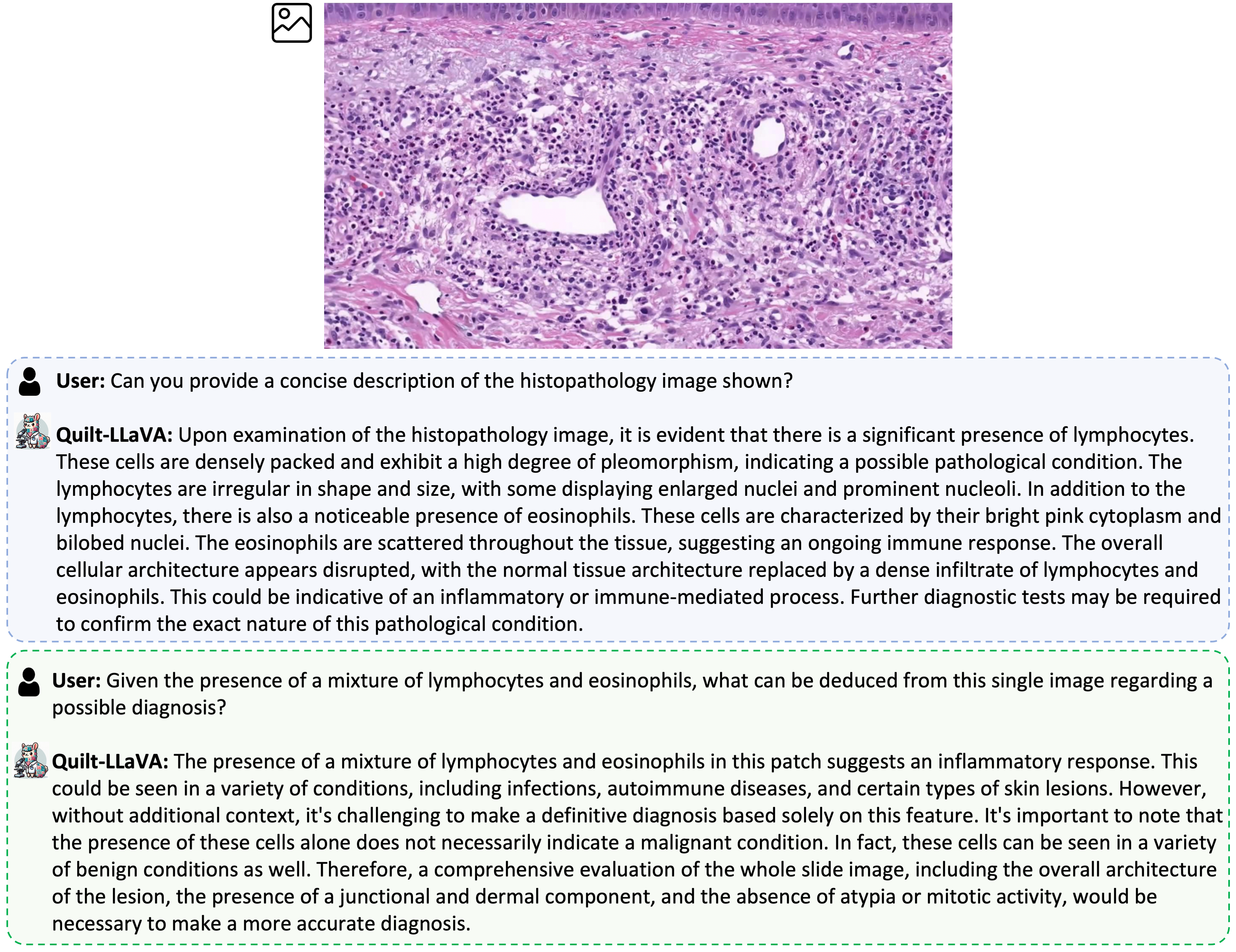
In iterative abductive reasoning, we simulate a conversation between two GPT-4 agents, mimicking a scenario where a professional doctor uses our model to ask longer medically intricate questions about an image. The first agent, termed Human-GPT, is provided with a single image caption and is tasked with abductively reasoning about the possible diagnoses and the facts used to arrive at these conclusions. The second agent, referred to as the AI Assistant GPT, is privy to the diagnosis and facts, simulating someone who has viewed the WSI of this particular patient. The AI Assistant evaluates the accuracy of the abduction derived by Human-GPT and provides comments or hints at potentially overlooked details using its inherent medical knowledge while utilizing diagnosis and facts. The conversation continues back and forth until a conclusion is made or the conversation reaches to the upper limit.
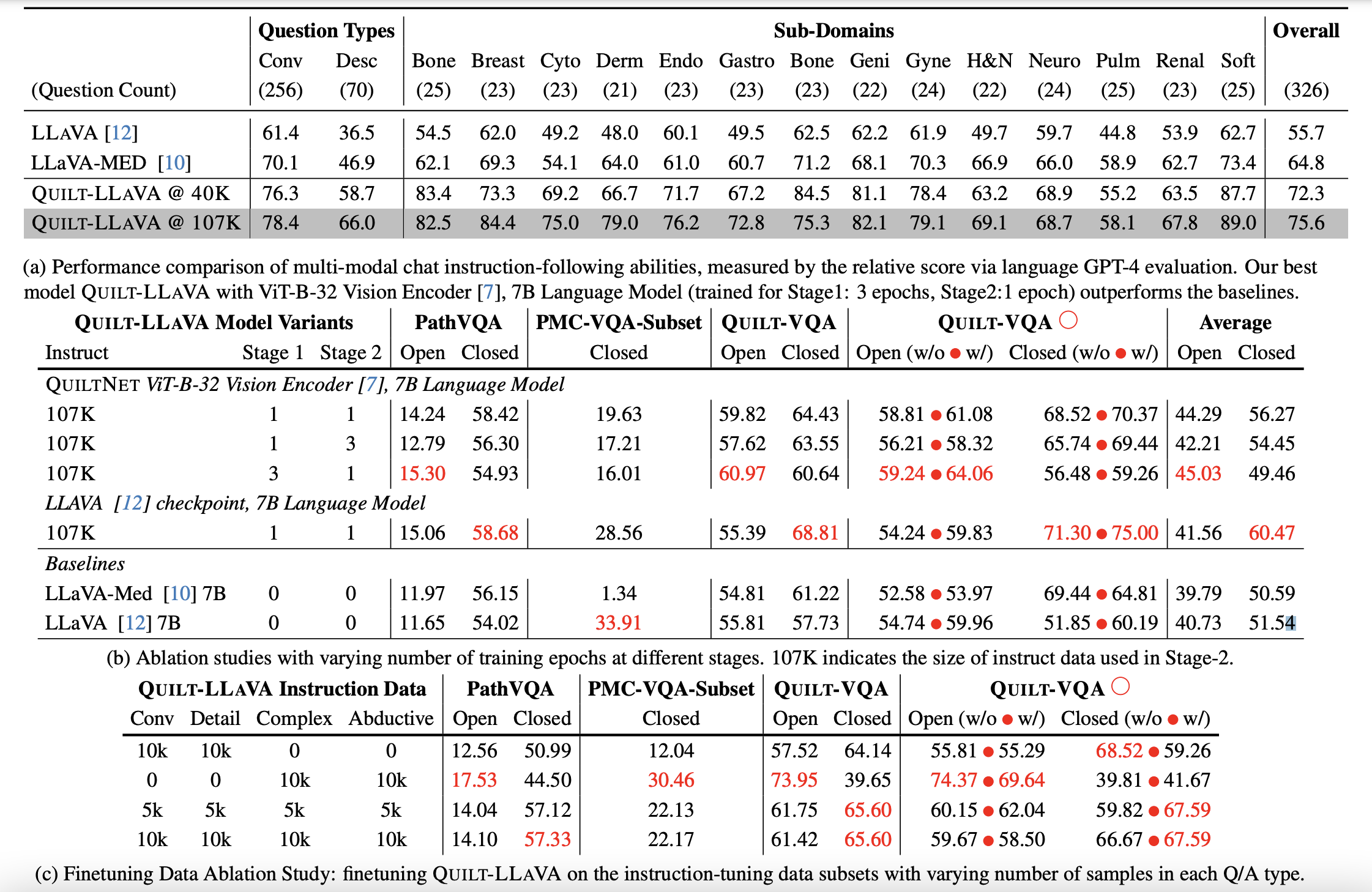
Some examples of detailed description and conversation based Q&A samples from the given description.


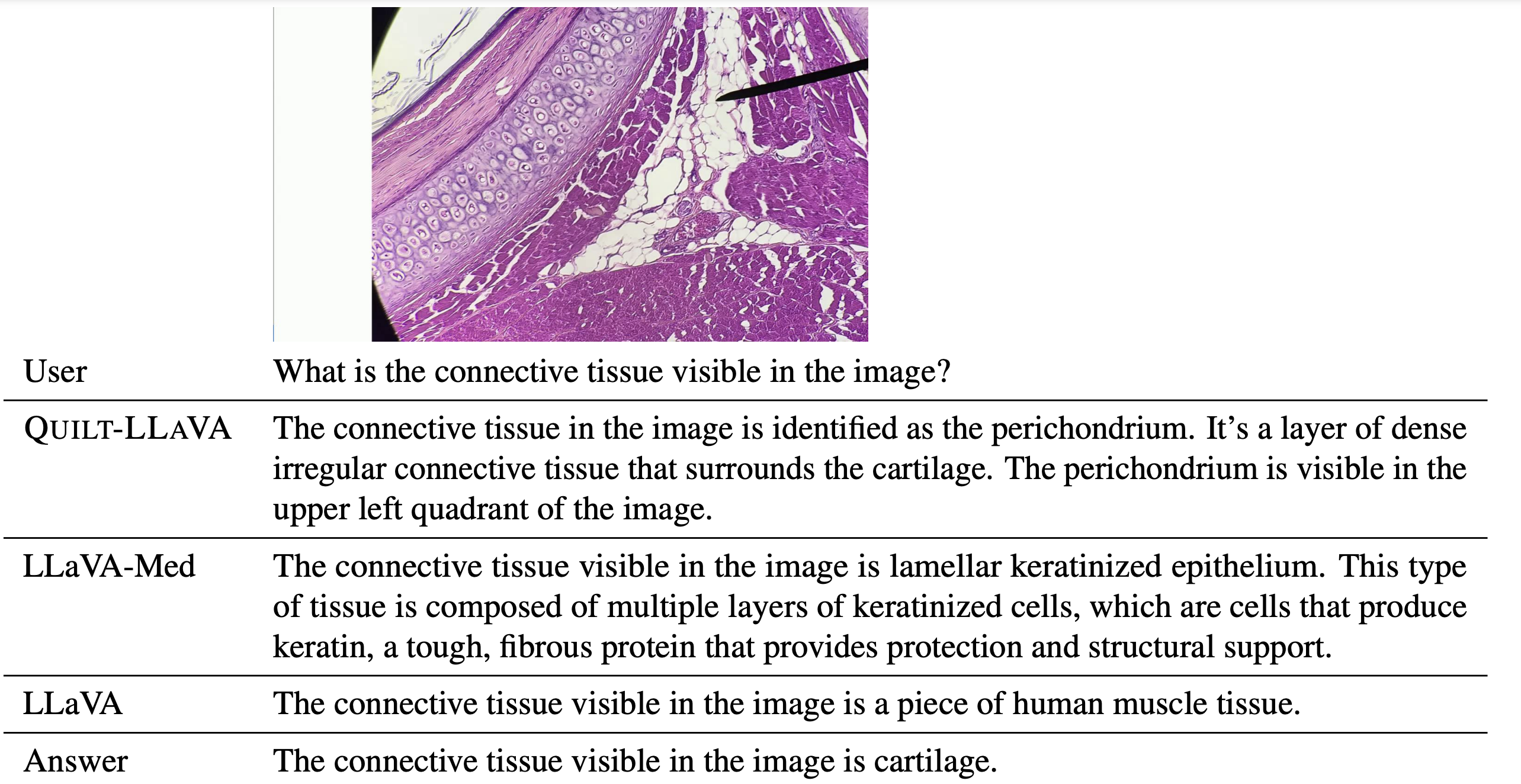
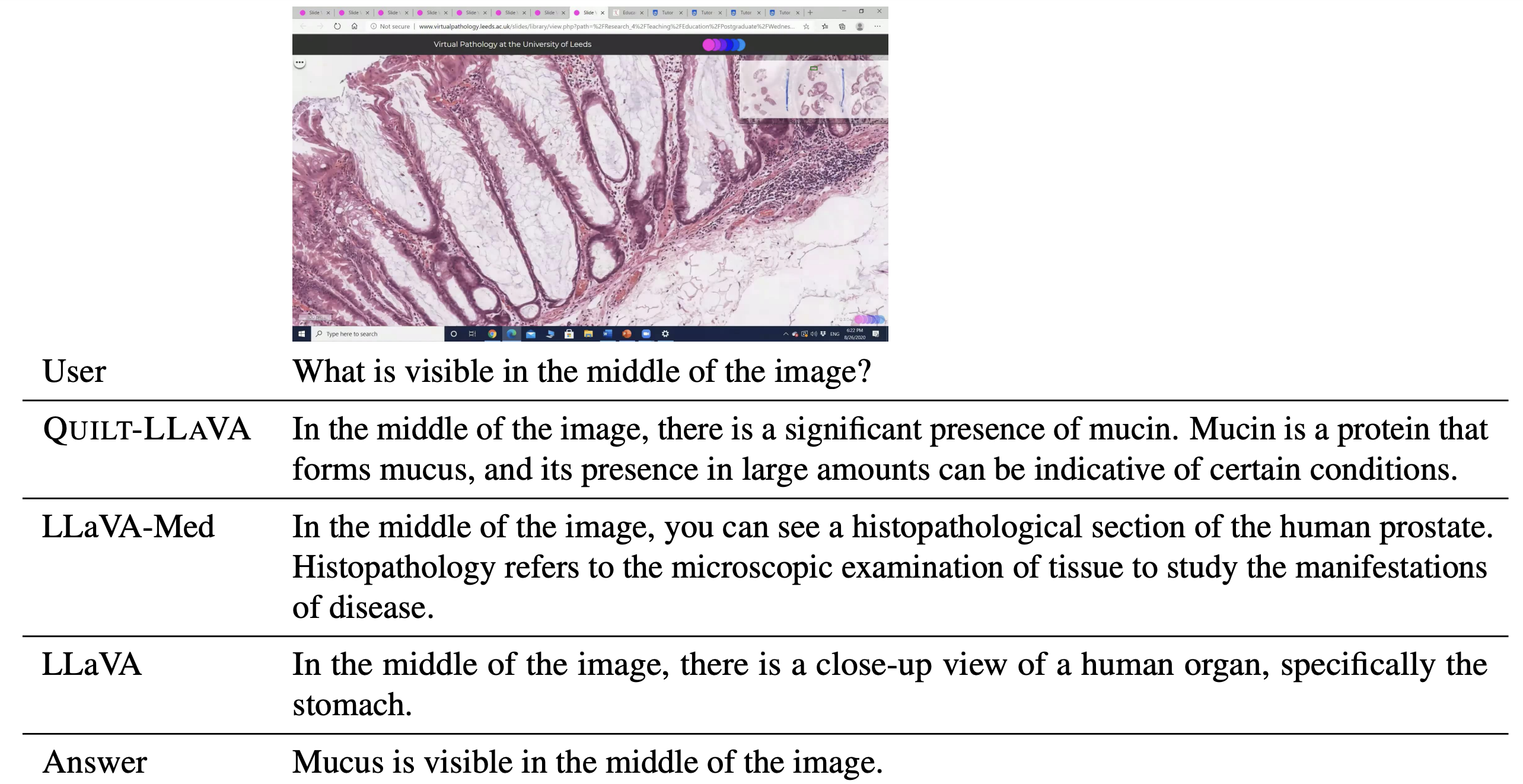
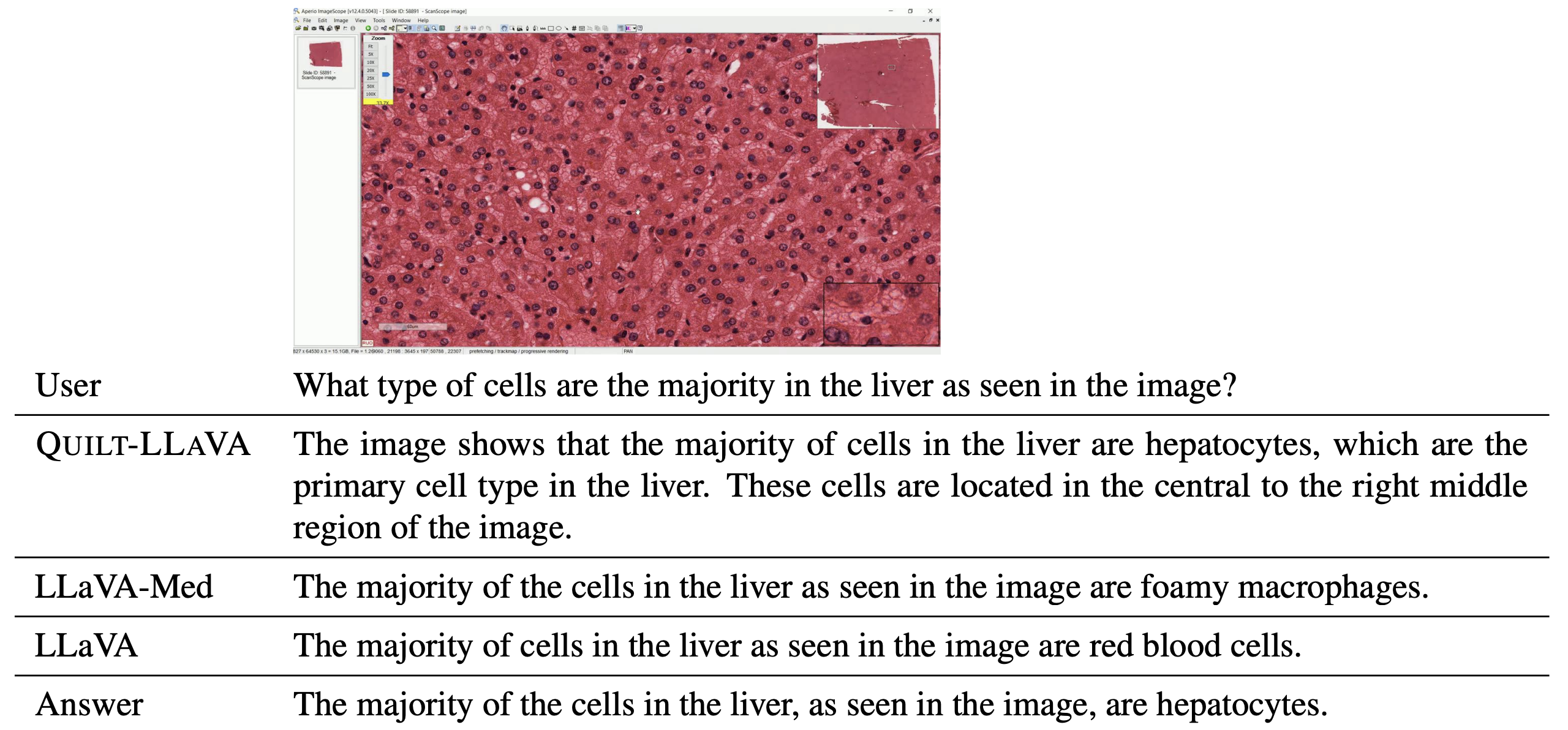
Some examples of reasoning-based Q&A samples generated from the given caption, along with the diagnosis and the facts leading up to that diagnosis, extracted from the broader video content.